|
|
|
|
News The Project Technology RoboSpatium Contribute Subject index Download Responses Games Gadgets Contact <<< Insta360 Air London Taxi TX2 >>> Using DC motors to power computersThe video about the ExperimentMotivationI started this experiment because:

I have purchased a Saito FA40 four stroke engine decades ago for a RC model plane that is scraped meanwhile after a couple of too hard ground contacts.The geared DC motors where left over from my WinchBot-Project and all other parts should be available in any good household... Setup
The generators I am using are in fact geared DC motors, left over from a project with my sponsor RS Components. The modern abacuses being powered during my experiments are a Raspberry Pi Model (?), a SIMATIC IOT2020 and an Arduino Uno. A 2x16 characters LCD is used to display results. Two geared DC motors are on my board with the test setup: 
The first motor, being driven by a hand crank has a transmission of 1:50 so that one revolution of the crank results in 50 revolutions of the generator. 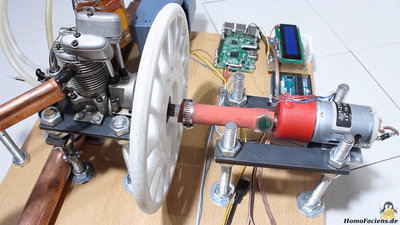
The second motor has a transmission of 1:2.5 and is driven by a 4-stroke model engine. The crank shaft is linked with the shaft of the DC motor through a pice of rubber tube. The shafts of both engines aran't perfectly in line and the rubber tube gives the linkage the needed flexibility. Furthermore it reduces the vibrations caused by the 4 stroke combustion process. Using a DC power supply I have recorded voltage and current of the used computing devices with the LCD, running my program:
ElectronicsParts list:The electronic components were left over from projects with my sponsor RS Components which is why links in the table point to their online shop.
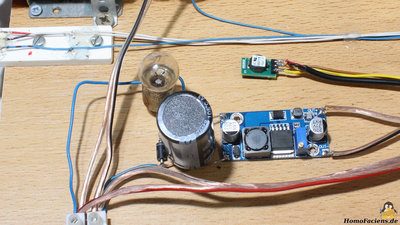
The output voltage of the motors, used as electric generators is boosted by a step-up converter to 12V for the SIMATIC and the Arduino and lowered by a step-down converter to 5V for the Raspberry Pi. A voltage divider composed of a 9.1V Zener diode and a filament bulb is at the input side of the DC converters in order to cut off peak voltages at the generator side. An electrolytic capacitor with a capacity of 10mF is used to smoothen the input voltage of the DC converters. 
With a Hall sensor and a magnet at the hand crank as well as on the motor couppling of the 4-stroke engine, the revolution speed can be detected. 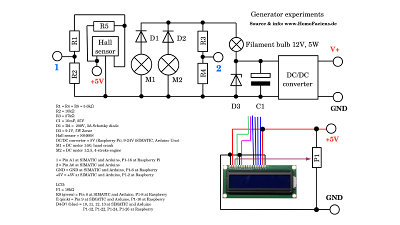
You can get the schematics and software as download package. <<< Insta360 Air London Taxi TX2 >>> News The Project Technology RoboSpatium Contribute Subject index Archives Download Responses Games Links Gadgets Contact Imprint |
|
|